Accelerating Digital Transformation with SD-WAN
Benefit from our agile & flexible approach to SD-WAN for optimal performance and service levels connecting sites, hybrid workers and clouds., a better way accelerates business initiatives and enables digital transportations
Agility
Increased bandwidth at a lower cost since the network traffic can be provisioned for optimal speeds and throttle low-priority applications
Intelligent
Centralized management across branch networks through a simple management console, which reduces the need for manual configuration and on-site IT staff
Visibility
Full visibility into the network, as the controller gives operators a holistic view of the network
Flexible
More options for connection type and vendor selection, since the network can reside on cost hardware and use both private and public connections to route its traffic.
Technological changes drive the new SD-WAN solutions
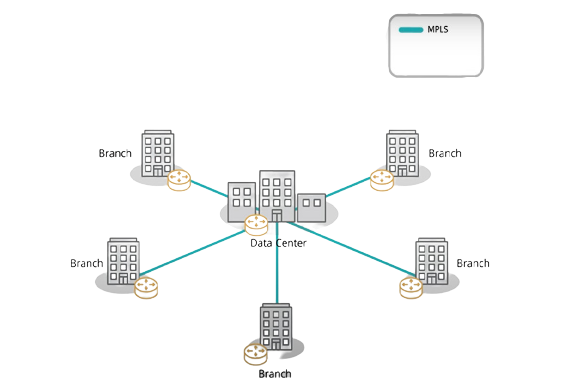
Let’s start by looking at the way we’ve built WAN for the past two-plus decades. Branch offices ,where more than 80% of transactions are handle, business were connected to a headquarters-based data center by a router over a leased line connection-usually MPLS. And that model was fine back then, because all applications were hosted in Interprise Data center. traffic was routed from sources to destination based on TCP IP addresses, access control list table and complex routing protocols all of the control functions was distributed across all the routers.
The traffic patterns have changed with the introduction of applications moving to the cloud, this could be enterprise apps that are now hosted in Amazon web services or Microsoft Azure or Google cloud or software-as-a-service apps like Office 365 Box, Dropbox and even Facebook and more
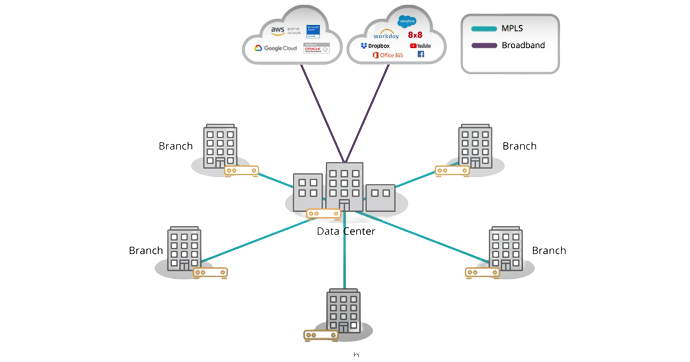
Sending Cloud traffic that is destined for the internet back to headquarter simply doesn’t make sense. It add delay that degrade application performance and it consumes costly leased line bandwidth.
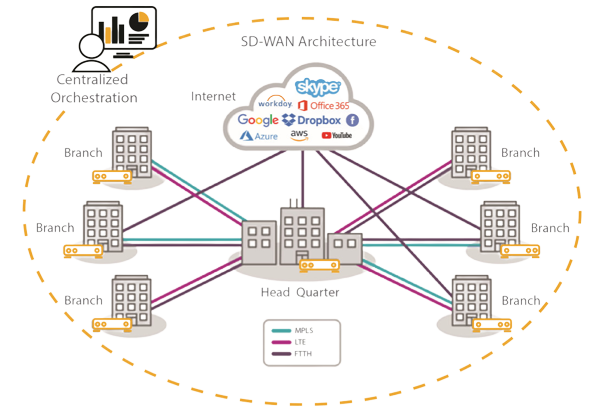
Why not use the internet to reach apps that are hosted on the internet this has driven the need for more intelligent software-driven or software-define model for the WAN – SD-WAN
What Is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN (Software Defined Wide Area Network) – A connection service management platform that provides functions of cross-domain networking and value-added services.
- Software-defined cloud connection platform;
- Intelligent routing on the platform side shields Internet jitter;
- Zero Touch Deployment (ZTP)
- Optional WAN acceleration value-added services;
- Data transmission encryption, support “national secret” algorithm
- Single entry management simplifies operation and maintenance

Why Do We Need SD-WAN?
Traditional network is based on completely hardware network devices which mostly rely on Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) for resilient and efficient network traffic flow.
Technology Pain Points:
- High end coordination costs, poor timeliness, poor flexibility, and simultaneously face the pressure of cross-industry competition from OTT vendors.
- Lack of capability to open interfaces, unable to achieve invocation and user self-service, poor multi-service collaboration efficiency.
What SD-WAN can do?
- Adopt the service leasing model, no need to purchase equipment;
- The price is much lower than the traditional dedicated line, the network quality is close to that of the dedicated line;
- Users can purchase services according to actual needs and increase or decrease flexibly;
- Use high-strength encrypted channels to achieve end-to-end encryption;
- Centralized management, no need for dedicated maintenance, reducing labor costs.
Ready To Get Started?
Uses Cases
Retail Chains
Increased bandwidth at a lower cost since By deploying SD-WAN, customer will able to upgrade its network to cope with new retail applications such as streaming and AR/VR
Intelligent Banks
The combination of 5G and SD-WAN will offer more diversified flexible access options for intelligent banks
Healthcare
Leveraging SD-WAN to Connect Healthcare Systems across Cloud, Data Center, Branch, and Edge
Financial Institution
SD-WAN offers simplicity cost savings, scale, application performance, security, visibility, and investment protection
University
SD-WAN is best defined as traffic monitoring and management from physical devices to the application itself
Hospitality
SD-WAN offers a seamless network deployment as it does not require any “rip” of equipment before “replacing” it with its own technology.
Partners



